Medical Stainless Steel
In the demanding world of healthcare, where sterility, durability, and biocompatibility are non-negotiable, one material consistently rises to the challenge: **Medical Grade Stainless Steel**. This specially formulated alloy is the unsung hero behind countless surgical instruments, implants, diagnostic equipment, and hospital infrastructure. Its unique properties make it indispensable for critical applications where human life and well-being are paramount.
Why Medical Stainless Steel?
Medical environments present unique challenges:
1. **Biocompatibility:** Must not cause adverse reactions when in contact with tissues or bodily fluids.
2. **Corrosion Resistance:** Must withstand aggressive cleaning agents, disinfectants (like chlorine), bodily fluids (blood, saline), and sterilization processes (autoclaving - high heat, steam, pressure) without rusting or degrading.
3. **Strength & Durability:** Instruments must withstand repeated use, sterilization cycles, and precise manipulation without bending or breaking. Implants require long-term structural integrity.
4. **Ease of Sterilization:** Must tolerate high temperatures (autoclaving ~135°C/275°F), chemical sterilants (EtO, hydrogen peroxide plasma), and radiation without damage.
5. **Non-Magnetic (for some applications):** Essential for MRI compatibility.
Medical stainless steel alloys are engineered specifically to excel in these areas.
Common Grades & Key Properties
| **304 / 304L** | Austenitic | Good corrosion resistance, excellent formability, non-magnetic. Economical. | Surgical trays, bowls, basins, cabinets, furniture, non-critical instrument parts. |
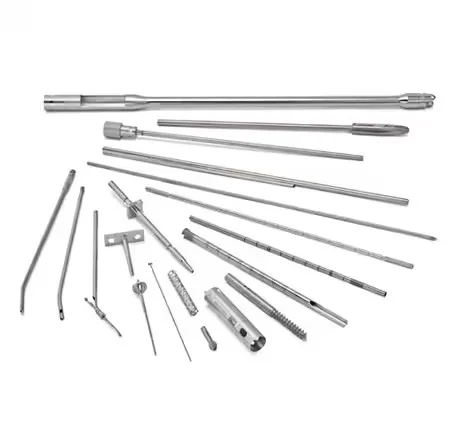
| **316 / 316L** (**Surgical Stainless Steel**) | Austenitic | **Superior corrosion resistance** (Mo addition), excellent biocompatibility, non-magnetic, good strength/formability. **Most common medical grade.** | Surgical instruments (forceps, clamps, scissors), implants (bone screws, plates), catheters, needles, endoscopes, sterilization containers. |
| **440C** | Martensitic | Very high hardness and wear resistance (can be heat-treated). Magnetic. | High-wear components like scalpel blades, dental burs, surgical stapler components, orthopedic cutting tools. |
| **17-4 PH** | Precipitation Hardening | High strength, good corrosion resistance, can achieve high hardness via heat treatment. | Specialist surgical instruments requiring high strength, orthopedic components. |
| **Nitinol** | Shape Memory/Superelastic | Unique ability to "remember" shape, extreme elasticity. Biocompatible. | Stents, guidewires, orthodontic archwires. *(Note: Often nickel-titanium, not strictly steel, but vital medical alloy)* |
**Key Mechanical Properties of 316L (Typical):**
* **Tensile Strength:** ~485 MPa (70 ksi)
* **Yield Strength:** ~170 MPa (25 ksi)
* **Elongation:** ~40%
* **Hardness (Rockwell B):** ~95 HRB
* **Density:** 8.0 g/cm³
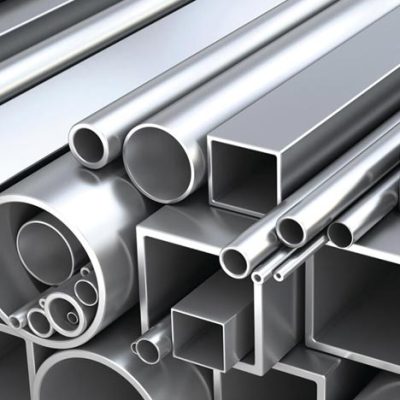
### Standard Dimensions & Forms
Medical stainless steel comes in a vast array of forms to suit diverse needs:
| **Sheet/Plate** | Thickness: 0.1mm to 20.0mm
Width: 100mm to 2000mm
Length: Custom (e.g., 2000mm, 3000mm) | Instrument bodies, casings, trays, implant backing plates, shields. |
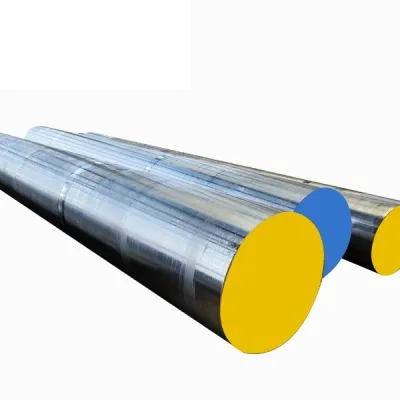
| **Bar (Round, Hex, Square)** | Diameter/Square: 1.0mm to 200mm
Length: 1000mm, 2000mm, 3000mm, 6000mm (or custom cut) | Machined instrument parts (handles, shafts), implant components (rods, screws), dental posts. |
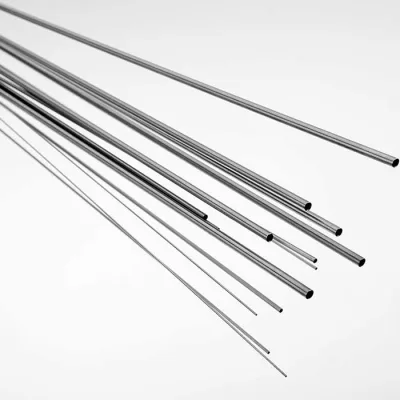
| **Wire** | Diameter: 0.01mm (ultra-fine) to 10.0mm
Spool lengths: Multiple meters/kms | Sutures, guidewires, orthodontic wires, springs, electrodes, mesh. |
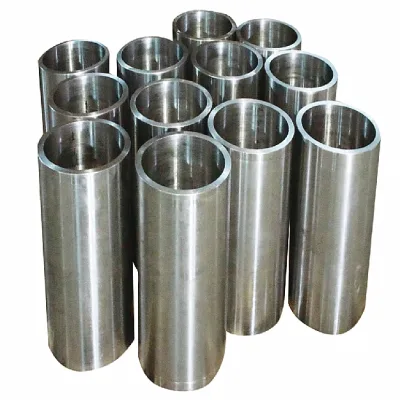
| **Tube** | Outer Diameter: 0.5mm to 100mm
Wall Thickness: 0.1mm to 5.0mm
Length: Custom | Cannulas, hypodermic needles, endoscopes, catheter shafts, fluid transport lines. |
| **Foil** | Thickness: 0.01mm to 0.5mm
Width/Length: Custom | Shielding, specialized sensors, thin diaphragms. |
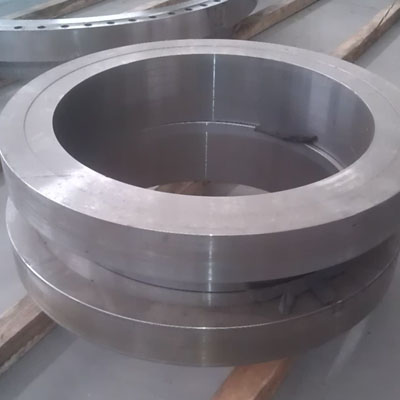
| **Forgings** | Custom shapes and sizes | High-strength, complex instrument/implants parts. |
*(Note: Tolerances for medical grades are often extremely tight, especially for implants and instruments.)*
Essential Product Information & Specifications
* **Certifications:** Must comply with stringent international standards:
* **ISO 13485:** Quality Management System for Medical Devices.
* **ASTM Standards:** ASTM F138 (316L for implants/surgical instruments), ASTM F139 (304L sheet/strip for implants), ASTM F899 (Spec for Stainless Steel Bar), ASTM A967 (Passivation). Many others cover specific forms and tests.
* **USP Class VI:** Plastics test standard sometimes used to indicate biocompatibility for metals used in medical devices.
* **REACH/RoHS:** Compliance with chemical restrictions.
* **Passivation:** A critical post-fabrication chemical process (e.g., nitric or citric acid bath) that removes free iron contamination and enhances the natural chromium oxide layer, maximizing corrosion resistance. *Required* for medical devices. Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and Mill Test Reports (MTR) detailing composition, mechanical properties, and processing history are essential.
* **Surface Finish:** Varies greatly: Mill finish, polished (various grits: #4, #7, Mirror), blasted (bead, satin), electropolished (EP). Choice depends on application (e.g., implant surfaces, ease of cleaning, aesthetic).
We also provide forging blanks and CNC precision machining services for our clients, covering industries such as energy, petrochemicals, steel, engineering machinery, plastics, prevention and control, hydraulics, healthcare, and food. Please feel free to send us drawings for inquiries.